A revolutionary new treatment solution for coronary inflammation.
Orticumab
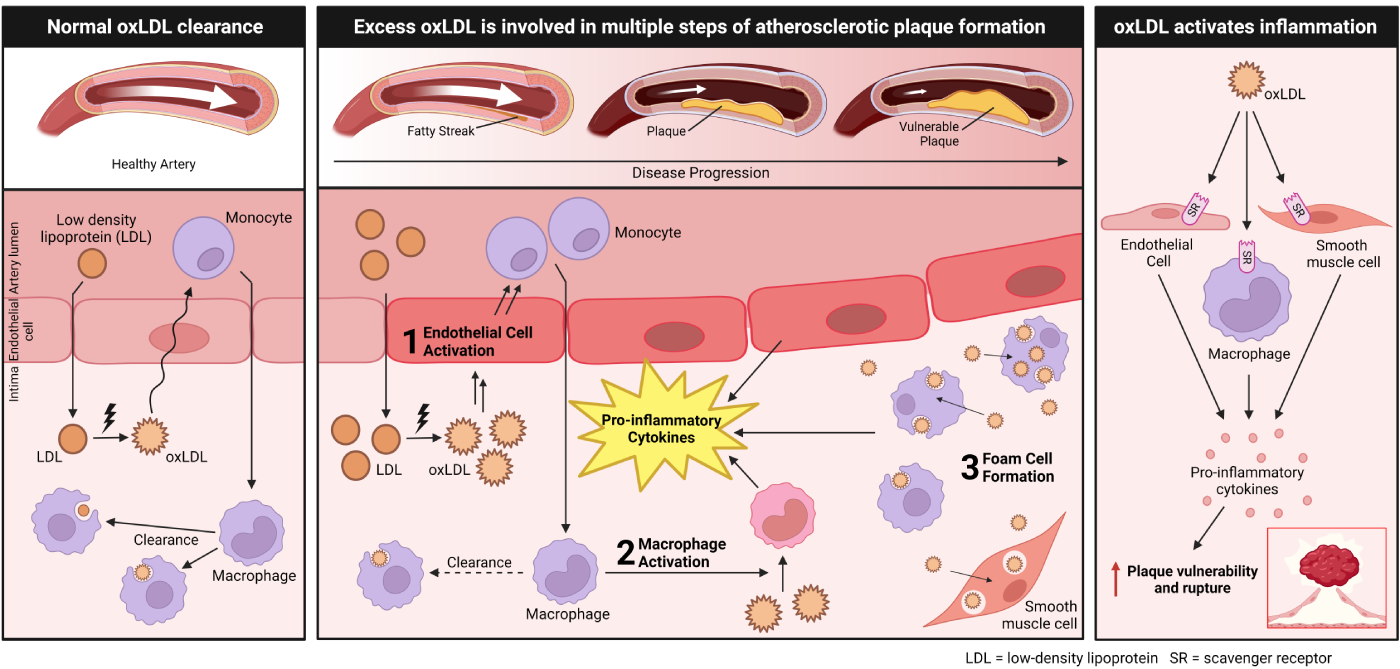
OxLDL Causes Coronary Inflammation And is Directly Linked to Risk of A Heart Attack
Orticumab: A First-in-Class Antibody Against Oxidized LDL (oxLDL), The Critical Driver Of Atherosclerotic Disease And Heart Attack
Orticumab is a fully human IgG1-type monoclonal antibody that recognizes and binds a specific oxLDL epitope, malondialdehyde (MDA)-modified apolipoproteinB-100.
Tissue-Specific Action
Mechanism of Action
The oxidation of LDL occurs in the arterial wall, where it then triggers inflammation and can lead to progression and rupture of atherosclerotic plaque. Orticumab works directly in inflamed coronary arteries, where oxLDL is abundant.
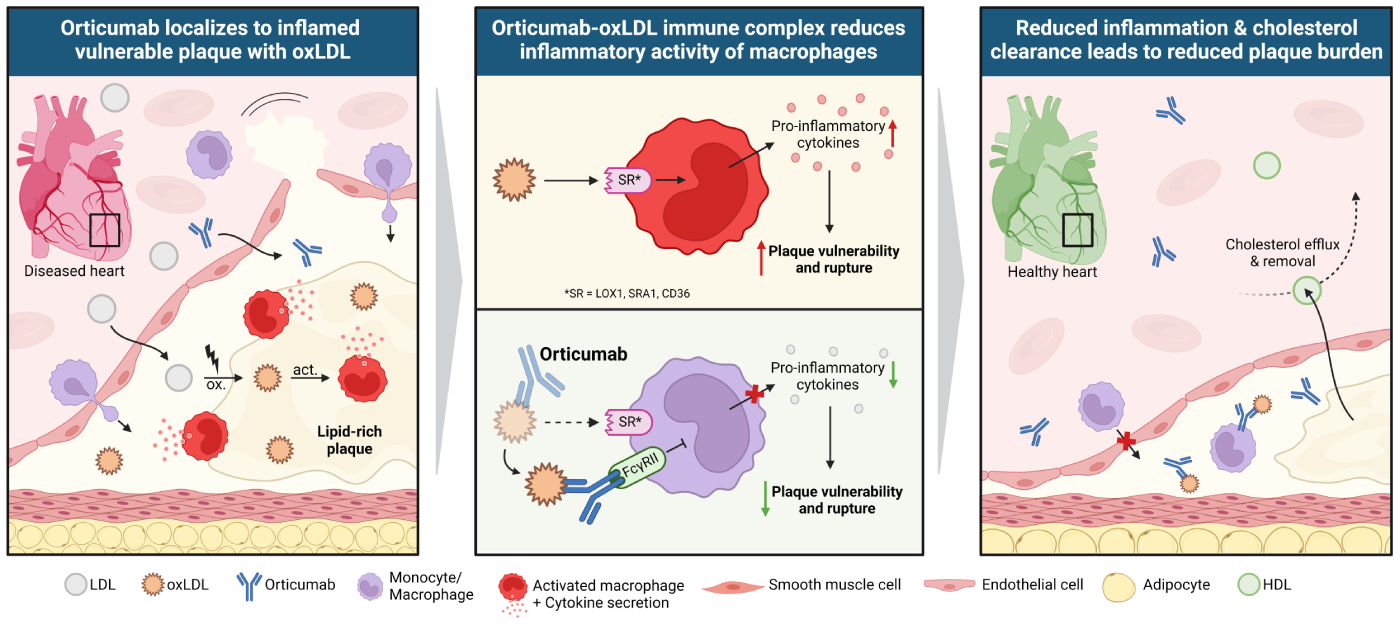
Orticumab Works Differently
A Highly Specific Approach to Coronary Inflammation.
When targeting coronary inflammation, specificity matters.
Comparison of Coronary Inflammation Targets
| oxLDL | Microtubule Polymerisation |
IL-6 | IL-1b | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Local vs. Systemic MoA | Local | Systemic | Systemic | Systemic |
| Role in Health (i.e. Immune Defense) |
No | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Role in CAD | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Class Inhibitors in CAD | Orticumab | Colchicine | Ziltivekimab | Canakinumab |
| Highest Development Phase in CAD | Phase 2 | Marketed | Phase 3 | Phase 3 |
By contrast, oxLDL inhibition with orticumab acts directly at the site of coronary artery inflammation. This localized and targeted approach may not only enhance treatment efficacy but also may minimize safety risks, making it an appealing therapy for patients in need. Furthermore, orticumab has demonstrated excellent tolerability in more than 300 treated patients across 4 clinical trials.
Clinical Development
Orticumab for Secondary Prevention after Acute Coronary Syndrome
Inflammation spikes in the coronary arteries during a heart attack, and so do levels of oxLDL. Our clinical development focuses on the secondary prevention of recurrent cardiovascular events in patients with prior acute coronary syndrome event, including heart attack.
Orticumab Reduced Coronary Inflammation
In a pilot phase 2 study, orticumab exerted anti-inflammatory effects on the coronary arteries of patients with psoriasis and elevated coronary inflammation (A), leading to a ~50% relative reduction of the predicted risk for fatal cardiac events by the CaRi-Heart® medical device (B).
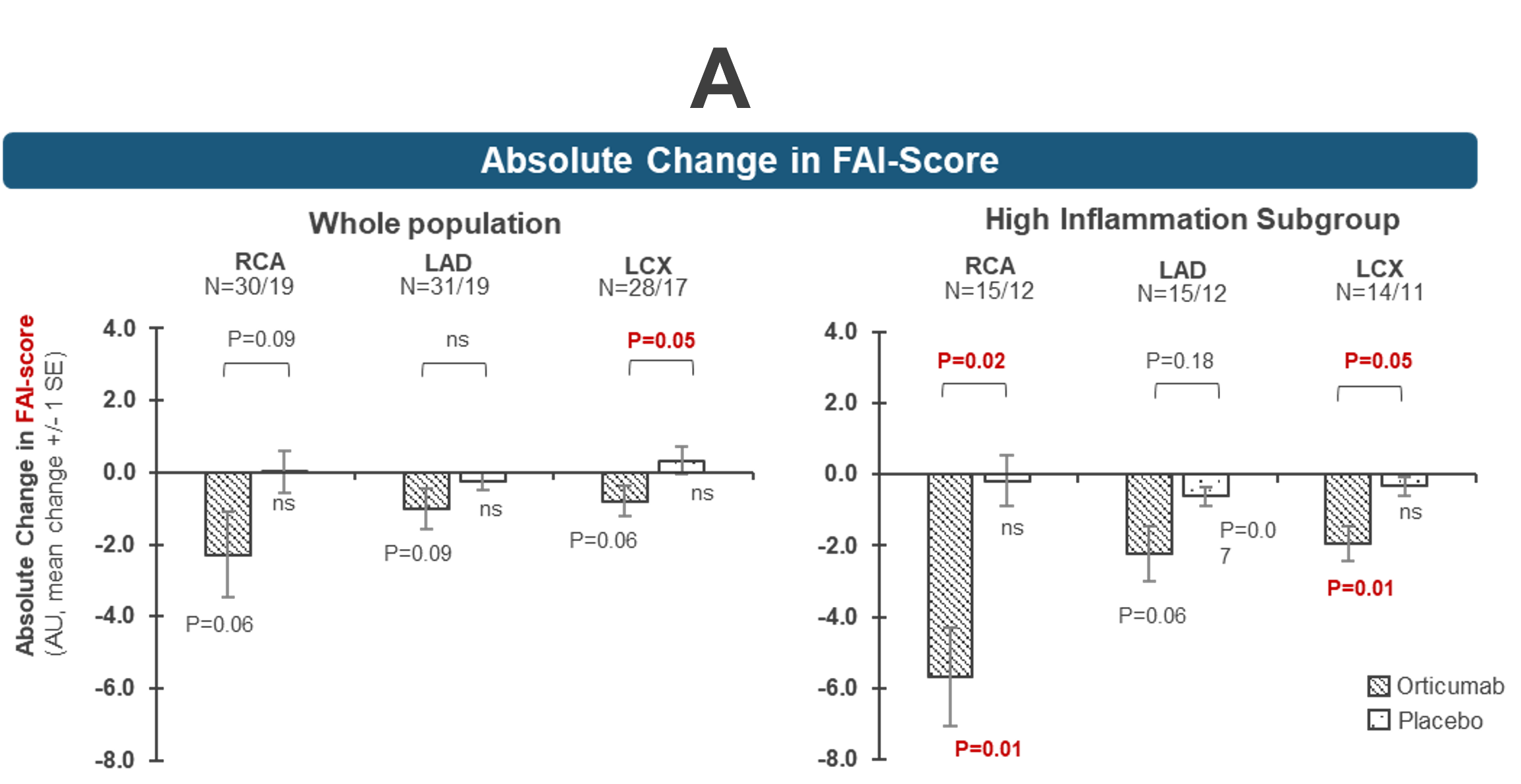
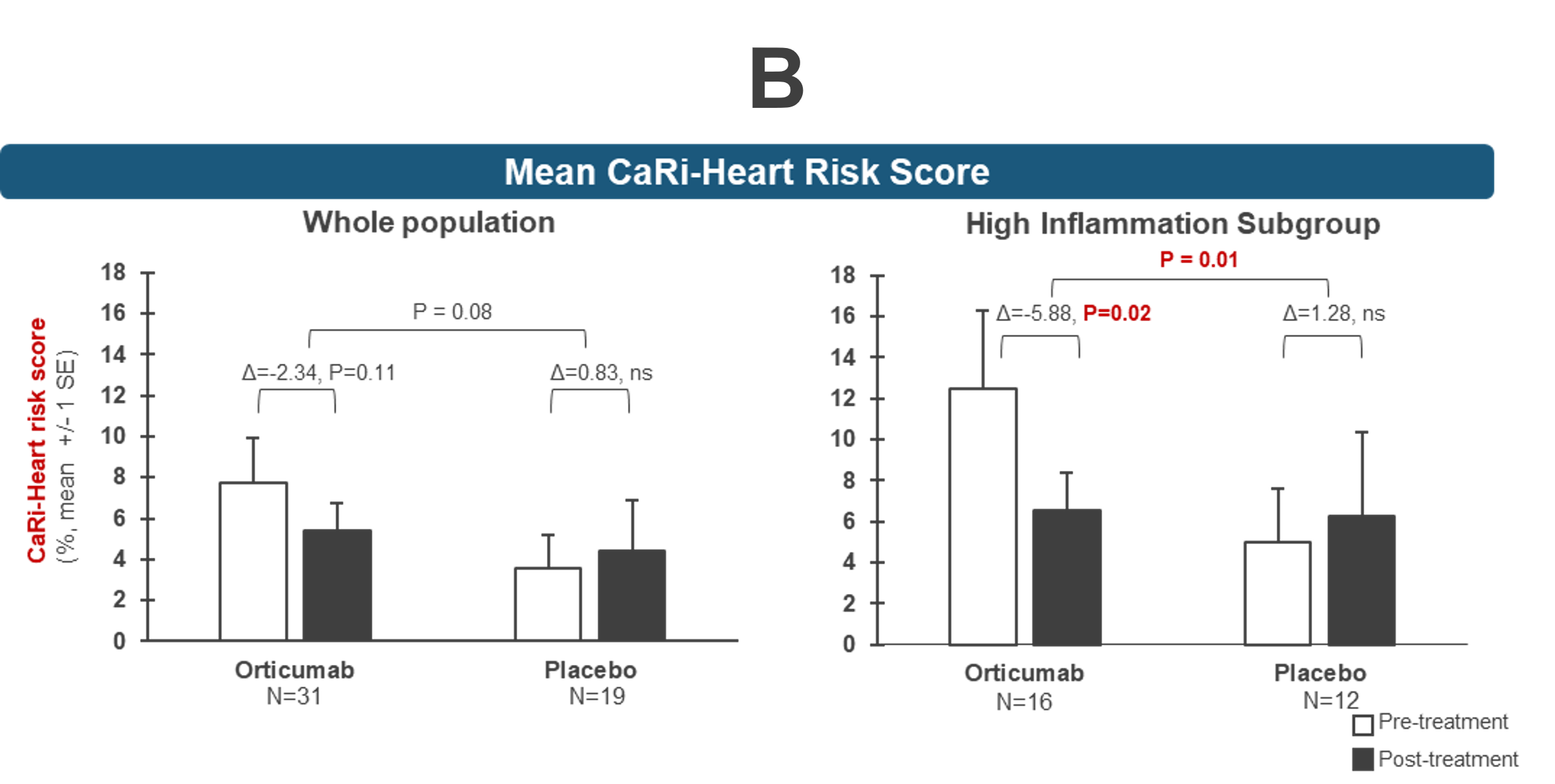
The CaRi-Heart® medical device (offered by Caristo Diagnostics) uses AI technology to measure coronary inflammation (FAI-Score) and predict risk of a fatal attack (CaRi-Risk). For more information, please read our recently published paper in the European Society of Cardiology’s Cardiovascular Research.
Orticumab in Featured Publications
Below, find some of the most recent and relevant mentions of Abcentra and Orticumab in prestigious industry publications.
Farina, Christopher J. et al, 2025, Current Opinion in Lipidology August 2025
Li, S. et al, 2013, Molecular Metabolism Volume 2, Issue 3, August 2013, Pages 256-269
Goncalves et al, 2009, Atherosclerosis Journal Volume 205, ISSUE 1, P96-100, July 01, 2009
Strom et al, 2007, Atherosclerosis Journal Volume 190, ISSUE 2, P298-305, February 01, 2007
Schiopu et al, 2007, Journal of the American College of Cardiology Volume 50, Issue 24, December 2007
Schiopu et al, 2004, Circulation, American Heart Association Journals Vol 110, Issue 14. October 5, 2004
Farina et al, 2024, European Society of Cardiology, Cardiovascular Research March 25, 2024
Farina, Christopher J. et al, 2025, Current Opinion in Lipidology August 2025